Valves
Sort by:
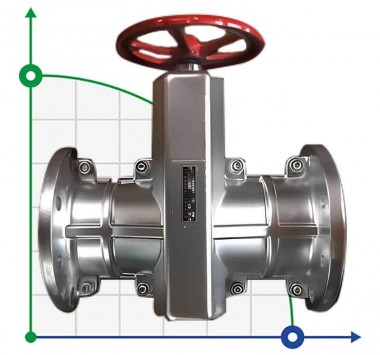
A valve is a type of pipeline fitting used to regulate or shut off the working fluid of a pipeline. Therefore, it has another name - valve valve.




Areas of use
This type of pipeline fittings is used to control the working environment in the “open” and “closed” modes. Less commonly, valves are used to regulate the force and speed of flow. Shut-off valves are most widely used in housing and communal services. Valves installed on pipelines for water, gas and wastewater ensure quick shut-off of pipelines in the event of an accident or the need for scheduled repairs.
Also, this fittings are actively used in various industries:
- Wastewater treatment and transportation;
- Food and chemical production;
- Pulp and paper production;
- Sphere of water treatment and water supply;
- Oil refining and gas production;
- Energy, production of building mixtures, etc.
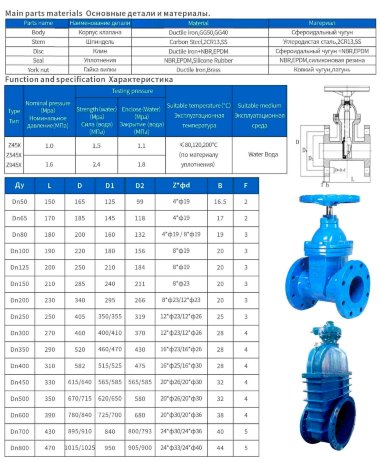
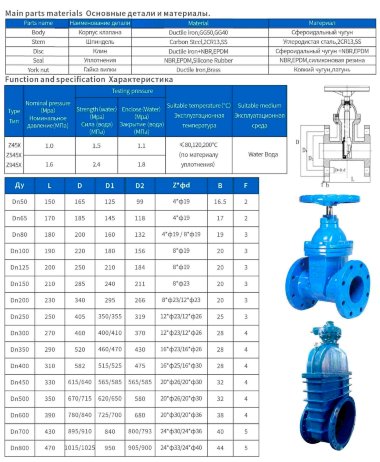
Based on materials
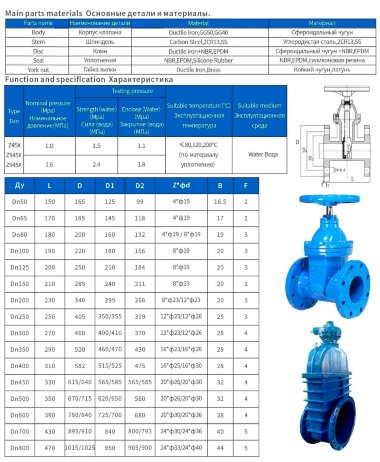
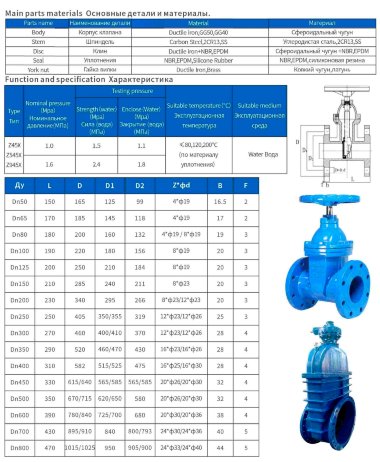
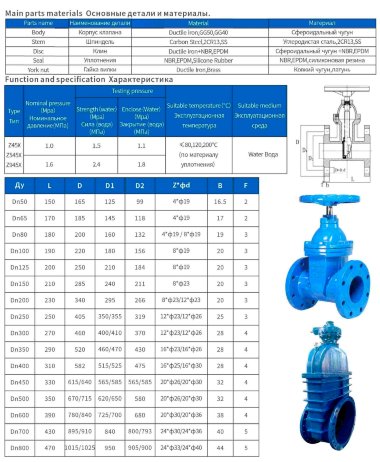
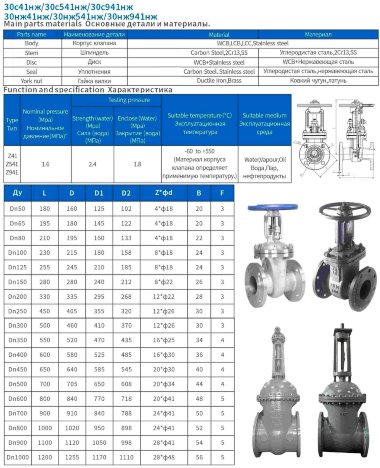
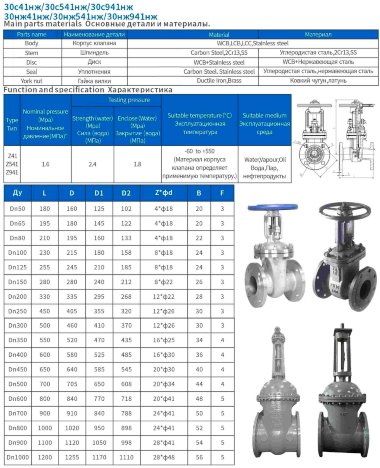
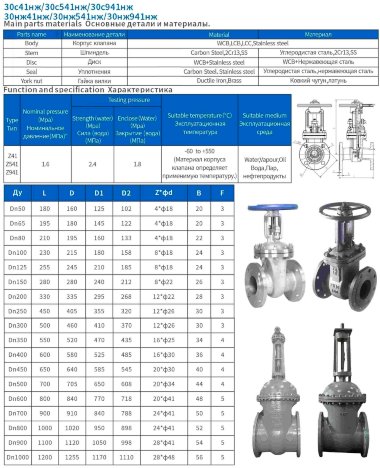
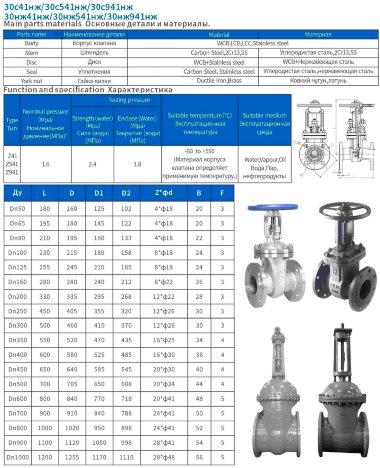
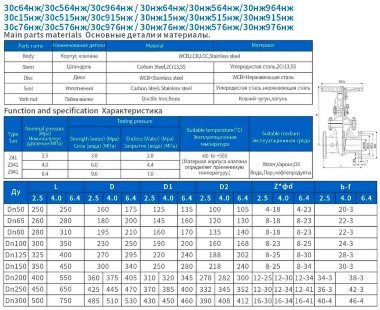
- Most valves have a solid cast body, which is made from the following raw materials:
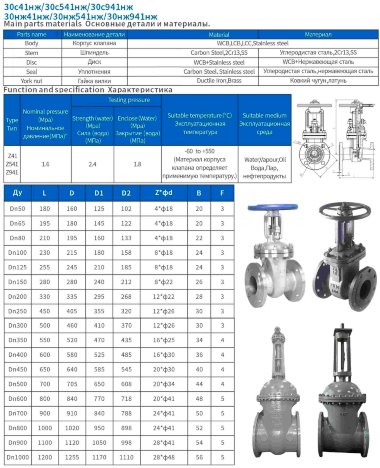
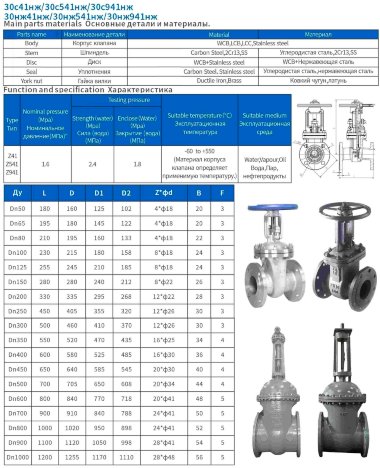
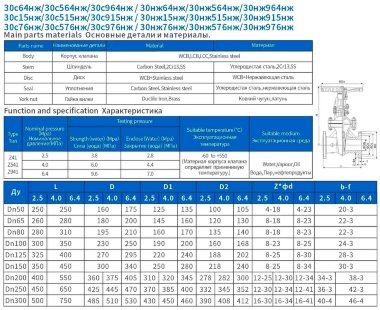
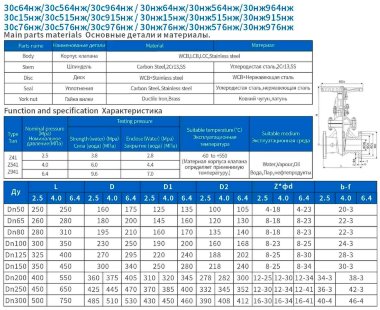
- Steel. More often it is carbon, stainless or alloyed. Steel models are designed for systems with a maximum temperature of +450°C and pressure up to 25 bar;
- Brass. Designed for household systems and pipelines with aggressive environments. Withstands temperatures up to +105°C and pressure up to 16 bar;
- Cast iron. It can be ordinary (gray) and malleable. Fittings made from this material are used in systems with non-aggressive environments, temperatures up to +225°C and pressures up to 10 bar.
By shutter type
- The damper, which will ensure the flow is blocked, is prepared in three versions:
- Klinova. It takes the shape of a wedge with two saddles, molded under the cut. They come in tough and gum (spring), whole or fluffy;
- Shibernaya. It is represented by a knife plate made of sheet metal. Follows the guillotine principle;
- Dvodiskova. It consists of two flat disks, moved in parallel one to one.
According to the movement of the rod
- There are two types of shutter control mechanism:
- Retractable. The screw pair is located outside the housing and is isolated from the working environment. When the damper is opened, the rod rises to a height equal to the diameter of the passage. This requires free space for the steering wheel to rotate comfortably;
- Non-retractable. The screw pair is located inside the housing in direct contact with the working environment. In the "open" and "closed" modes, the height of the rod remains unchanged. This allows you to install the valve in hard-to-reach places.
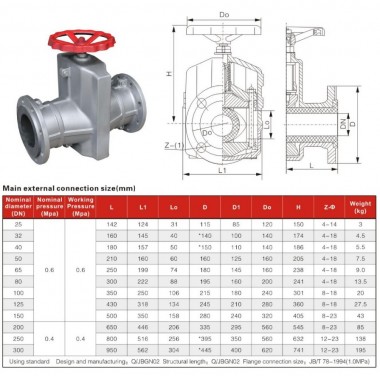
By type of connection
- The valve can be attached to the pipeline in the following ways:
- Coupling connection. This is done using threaded fittings. Typically used in small diameter systems;
- Flanged. Flat round flanges are welded at the valve inlets, which are connected to similar elements on the pipe using bolts and studs;
- Wafer. The valve is installed on a pipe between two flanges, which are tightened using studs and nuts.
Sale