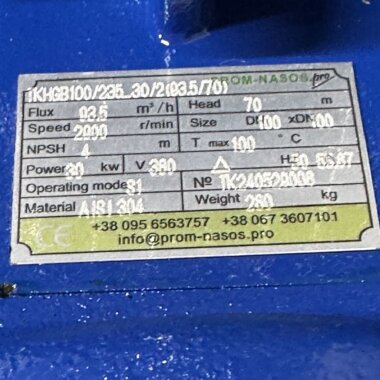
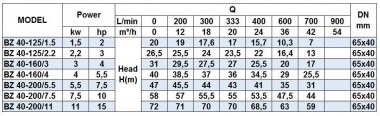
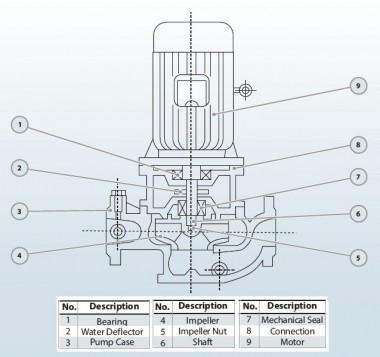
Prospects of the bioethanol, alcohol plants

The production of ethyl alcohol (ethanol) is an important component in global industrial production. Produced from any raw material that contains polysaccharides, disaccharides and monosaccharides. Ethanol is divided into types depending on the final purpose of further use: rectified, dehydrated, raw alcohol, distillates. Rectified ethanol is used for the production of alcoholic beverages (vodka, tinctures), pharmaceuticals, and perfumes. Dehydrated alcohol is mainly used for fuel production (E5-E85). Raw alcohol and distillates are used for the production of whiskey, cognac spirits, brandy, cognac, tequila, rum, etc. The quality of ethanol (concentration of impurities and organoleptic assessment) is regulated by the relevant regulations (EN, GOST, DSTU, etc.)

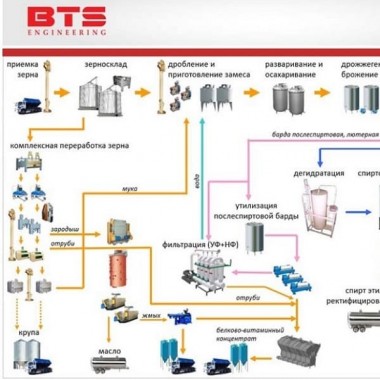
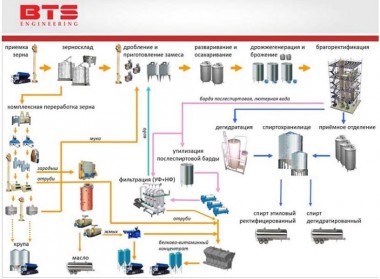
Below is an example of the technology for producing ethanol from starch-containing raw materials.

Acceptance and preparation of grain for processing
Grain is taken to the unloading device. All raw materials that are supplied to the enterprise are cleaned from organic and mineral impurities. This process is carried out on grain cleaning machines of various types.

Grain grinding
The efficiency of processing of raw materials at hydroarsination treatment depends on the degree of destruction. For grain grinding, devices (crushers) are recommended for use, which guarantee grinding of 96...98 % — passage through a sieve with a hole diameter of 1 mm.
Preparation of the batch

This operation is performed by mixing the resulting grinding with water in a special device that is installed directly above the collection for preparing the batch. In this collection there is an active stirring of the medium by means of a stirring device (stirrer) of various designs and configurations. The temperature of the batch is maintained by using distillery dreg filtrate and/or hot water for its preparation. At this stage, the process of swelling of starch grains and rarefaction of raw starch begins due to the action of a diluting enzyme preparation — alpha-Amylase containing a thermostable α-amylase.
Hydrodynamic and enzymatic processing of the batch
The main process of starch decomposition and dextrinization is carried out in two sequentially connected devices equipped with devices for mixing. The temperature mode of batch processing at this stage is maintained automatically by supplying steam to the bubbler of the GDFO No. 1 apparatus. From the gdfo No. 1 unit, the wort enters the GDFO No. 2 unit through an overflow PIPELINE and then into the fermentation Department.
Yeast generation

This process consists of two stages:
- breeding of pure culture (dry) yeast (laboratory stage);
- the growing production of yeast
It is also possible to use dry yeast directly in the fermentation process.
Cultivation of production microorganisms lasts until the product accumulates in them within 3.0-4.5% vol., which corresponds to the apparent density of production microorganisms - 2/3 - 1/2 of the initial concentration of dry substances in the syrup.
Mixing the medium in production machines during cultivation - reduces the duration of the process by almost half.
sowing, and the remaining volume is transferred to fermentation.
Fermentation

The main producers of alcohol in the processing of starch-containing raw materials are the microorganisms Sacharomyces cerevisiae. For the cultivation of industrial microorganisms, a cooled boiled mass is used after hydrodynamic enzymatic treatment, an enzyme preparation of glucoamylase action is added.
Fermentation involves the process of accumulation of alcohol in the brew in special devices (fermenters) and is implemented in a battery of fermenters of periodic or continuous action.

The duration of fermentation depends on the method of its implementation, the type and quality of raw materials, wort concentration, medium temperature, dosage of the enzyme preparation and is 48...72 hours.
Distillation and rectification
The brew after heating in the brew heater and separation of carbon dioxide in the CO2 separator is sent to the feed plate of the brew (distillation) column, then — BC.
In the Mash column, the volatile part of the brew is separated from the non-volatile part. The brew, freed from the volatile part, is output from the lower part of the MC in the form of the distillery dreg. With it, extractive substances, suspended solids, a significant amount of water and tail impurities are removed. The volatile part of the mash containing ethyl alcohol, water, and accompanying volatile impurities, in the form of a mash distillate, is sent to the power plate of the epuretion (hydroselection) column, then —EC.
In the EC, head impurities are isolated in the form of HFOEA (the head fraction of ethyl alcohol) and the epyrate is removed from the lower part, which is fed to the feed plate of the distillation column, then to the RC.
In the Rectification Column, further purification occurs with the release of head and end impurities — in the form of unpasteurized alcohol, and intermediate impurities — in the form of fusel oil and strengthening (concentration) of ethanol to the normalized values.. Luther water enriched with tail impurities is removed from the lower part of the RC, and rectified alcohol is taken from the upper part.
To obtain high– quality alcohol ("Lux"), rectified alcohol is sent to the feed plate of the final purification column (methanol) - further FPC. In the FPC, the final purification of alcohol from the end impurities in the form of unpasteurized alcohol and intermediate impurities in the form of part of the alcohol taken from the FPC cube takes place. Rectified alcohol is taken from the upper part of the FPC.
To increase the yield of alcohol, relative to the theoretical one, the fusel fraction, wet refluxe, unpasteurized alcohol is sent to the collection and then to the feed plate of the acceleration column – then the AC.
In the AC, alcohol is extracted from a mixture of the fusel fraction and the wet refluxe, and the impurities are concentrated in the form of FEAC – fusel-ether-aldehyde concentrate. The cubic remainder of the AC (with an alcohol content of 6...12% by volume) is sent to the MC.

Dehydration
To obtain dehydrated ethanol, an adsorption process on molecular sieves is used. Raw alcohol is sent alternately to special containers filled with a special nozzle. Passing through the nozzle layer, ethanol is released from moisture and the final water content is reduced to 0.05% vol.
Membrane cleaning of dried distillers grains with solubles (DDGS)

All distillery dreg from the MC is consistently sent to:
- decanter plant, where it is divided into distillery dreg and cake filtrate
- a membrane installation where yeast-protein concentrate (YPC) is extracted from the distillery dreg filtrate)
Separated cake and yeast-protein concentrate are mixed to obtain a protein-vitamin concentrate (PVC).
PVC is then dried and sent in dry form to the warehouse and for sale, and the purified filtrate of the distillery dreg after pH correction is used to prepare the batch.
PVC drying
Use an air-drying unit that uses hot steam, natural gas, or solid fuel as a heat carrier to dry the PVC.