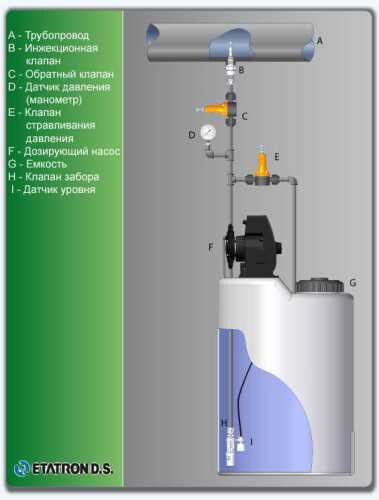
Automatic control and dosing of sodium hypochlorite
Flow chart

Currently, the disinfection of drinking water at the enterprise is carried out with the help of chlorine gas in bleach plants of the ejection type. The chlorine is supplied through a system of chlorine pipelines to clean water tanks, where the chlorine gas comes into contact with drinking water.
Due to the fact that chlorine is a very toxic substance, and the transportation and storage of chlorine gas is explosive, its use poses a threat to service personnel and the population living near pumping stations, therefore, it is recommended to switch to alternative methods of water disinfection (ultraviolet light, sodium hypochlorite, ozonation, etc.). Of the listed methods of water disinfection, only chlorine-containing substances have a decontaminating aftereffect for a certain period of time. Therefore, the most convenient and cost - effective way to decontaminate drinking water is to use a solution of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO).
Characteristics of sodium hypochlorite
The most reliable and economically feasible method of disinfection of drinking water is its chlorination, and sodium hypochlorite refers to chlorine-containing reagents, which are characterized by the ability to preserve the decontaminating effect for a long time of water transportation through pipes, but at the same time is less toxic than liquid chlorine. Sodium hypochlorite is the least toxic and deficient, relatively cheap compared to other reagents containing active chlorine.
A solution of sodium hypochlorite NaClO is obtained by electrolysis of table salt. The most stable solutions are sodium hypochlorite solutions at pH> 11. With sodium hypochlorite hydrates, the most stable is NaClO • 5H2O hydrate. The factors that affect the stability of sodium hypochlorite solutions include concentration and temperature.
Thus, solutions containing 250 g / l of NaClO lose half of the active chlorine at room temperature in 5 months, 100 g / l of NaClO in 7 months, 50 g / l in 2 years, and 25 g / l in 5 ... 6 years. At a temperature of 60 ° C, a solution containing 50 g / l of NaClO loses half of the active chlorine in 13 days, and at 100 ° C-by 5: 00.
When exposed to light, the speed of the NaClO schedule increases approximately twice. To increase stability, NaClO solutions are stored in the dark at a low temperature. If a certain amount of MgSO4 is added to the sodium hypochlorite solution, magnesium hydroxide precipitates, which captures heavy metal ions, increasing the stability of the hypochlorite. It is known that the stability of sodium hypochlorite increases in the presence of sodium silicate in the molar ratio Na2O: SiO2 from 1: 1 to 1: 2 ... 1: 3,5
The stabilizing effect on solutions of sodium hypochlorite is carried out by gelatin, casein or a mixture of them. For example, an 8% NaOH solution is chlorinated to a pH of 8.4 ... 8.6, then 0.3% gelatin is added and pH = 9.2 ... 9.4 is set. A stable solution containing 7.5 ... 8.0% NaClO is obtained. Sodium hypochlorite is produced in the form of solutions containing about 15% of active chlorine. For individual consumers, these solutions are diluted to 5 and 10%.
- Chemical and physical properties:
- chemical formula-NaClO;
- aggregate state: aqueous solution. Solid form - not stable. Upon contact with air, the product quickly turns into a liquid state;
- boiling point-decomposes at a temperature of more than 35 °C;
- 0.50 g/cm3;
- solubility in water-82% at t = 25 °C;
- hydrogen index-pH = 11;
- appearance-liquid from yellow-green to red;
- smell-sharp chlorine;
- volatility-during decomposition, chlorine, sodium oxide is released;
- reactivity - strong oxidizing agent, reacts with metals, causes corrosion of metals.
- Fire and explosion hazard:
- non-flammable explosive substance. Supports combustion, as it is a strong oxidizer (in contact with combustible organic substances-sawdust, rags and others in the process of drying can cause spontaneous combustion);
- temperature limit of flame propagation - does not burn;
- concentration limit of flame propagation - does not burn;
- possibility of thermal degradation, products of formation-chlorine, sodium oxide;
- fire extinguishing agents-are selected depending on the explosive and fire-hazardous properties of combustible materials located in the ignition zone together with this product, taking into account the presence of a strong oxidizing ability in hypochlorites;
- special fire safety measures-avoid heating up to 70 ° C and above (decomposition with explosion). Keep away from flammable materials.
- Toxicity:
- cumulative-weak.
- the clinical picture of acute poisoning is a sore throat, cough, arrhythmic breathing, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, confusion, coma, shock.
- the most vulnerable organs and systems are the central nervous system, respiratory system, liver, kidneys, pancreas, skin, eyes;
- doses (concentrations) with toxic effects:
- EDmin = 1000 mg / kg (person, IV once for action on the central nervous system);
- EDmin = 45 mg / kg (person, intravenous once for action on the central nervous system);
- skin-resorptive effect-no;
- sensitizing effect-yes;
- emdriotoxic effect - not studied;
- gonadotoxic effect-yes;
- mutagenic effect-yes.
- The effect of sodium hypochlorite on the human body:
- According to the degree of exposure to the human body, sodium hypochlorite of the "A" brand belongs to substances of the 3rd hazard class in accordance with GOST 12.1.007-76, as a moderately dangerous substance when administered in the stomach and to the 4th class of low-risk substances when applied to the skin, which causes moderate local irritation to the skin and pronounced on the mucous membrane of the eyes.
- Sodium hypochlorite in concentrations of 0.5-0.3% (according to the drug) with a single contact does not cause local irritation to the skin, in concentrations of 4-5% causes mild irritation. Repeated contact causes dry skin after 2-3 applications.
- The inhalation hazard of the substance is due to the release of chlorine into the air, which irritates the mucous membrane of the eyes and respiratory organs.
- The maximum permissible concentration in the air of the working area is 1.0 mg / m3 (hazard class 2 according to GOST 12.1.007-76)
- The maximum permissible concentration in atmospheric air is 0.1 mg / m3.
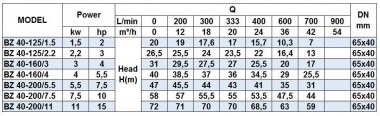
Calculation of the consumption of sodium hypochlorite solution
The calculation of the consumption of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO) is carried out for a 6% NaClO solution is given in tabular form.
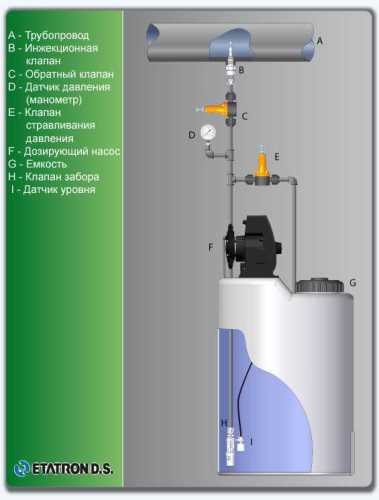
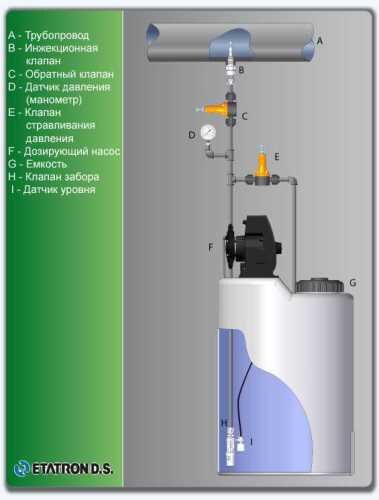
Technological equipment
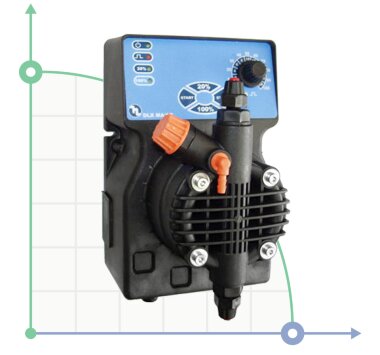
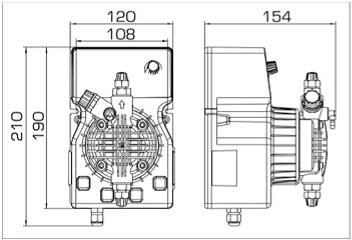
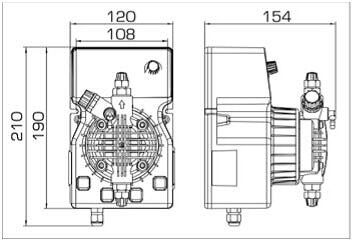
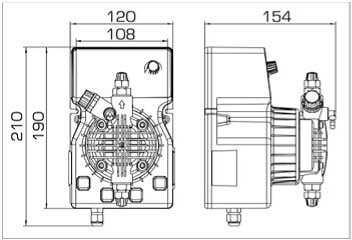
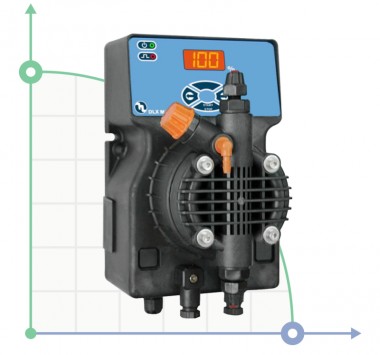
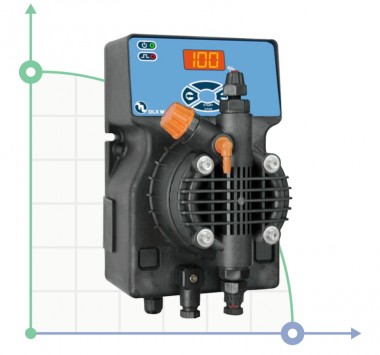
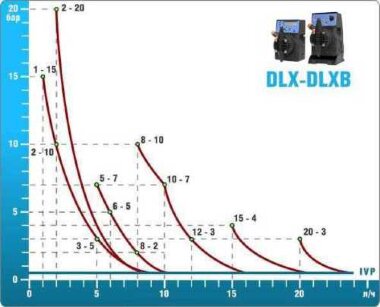
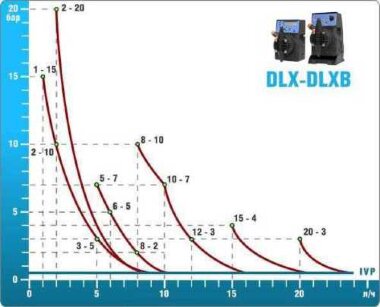
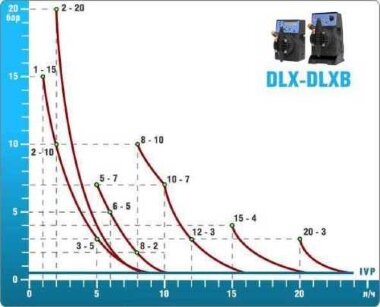
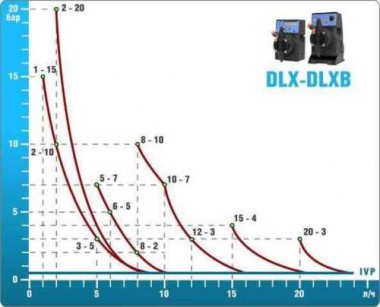
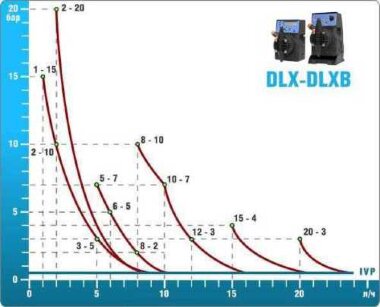
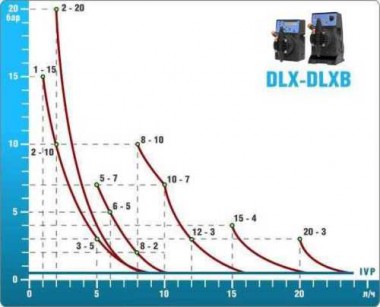
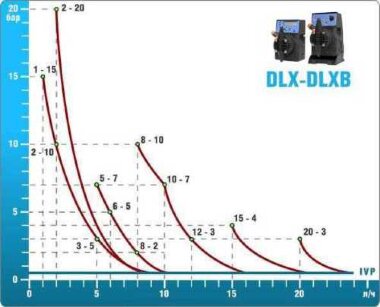
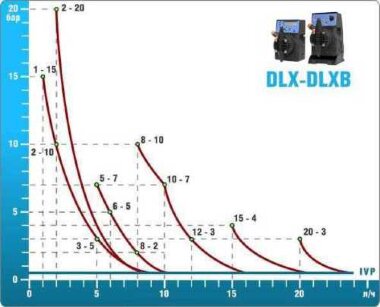
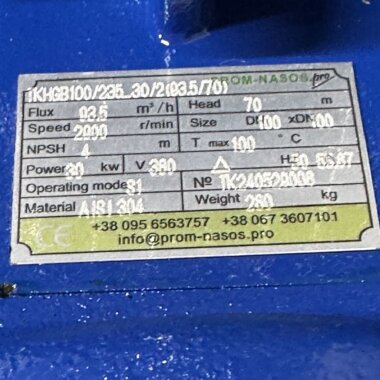
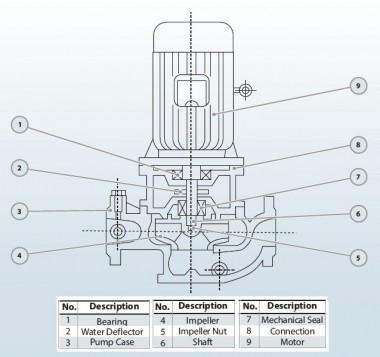
- According to calculations, ETATRON D.S equipment is used to control and dose the sodium hypochlorite solution.:
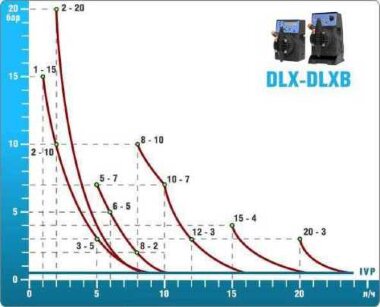
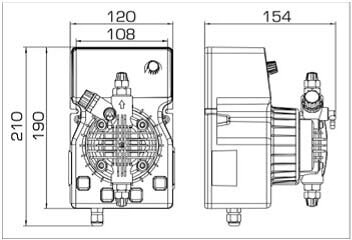
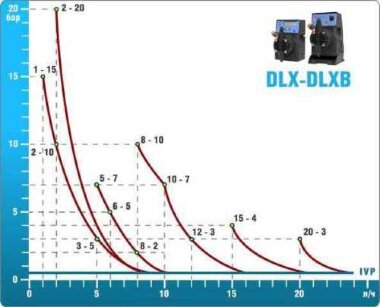
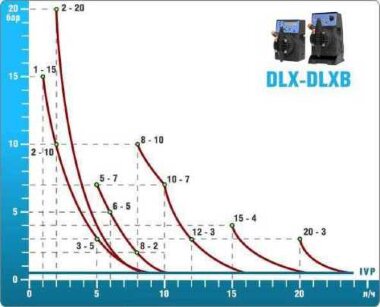
- metering pumps with a capacity of 16 l / h, 14 bar
The metering pumps are controlled by the Etatron eSELECT B1 chlorine controller. - The value of the chlorine dose is determined using the Etatron SCLO3 galvanometric chlorine sensor.
Depending on the chlorine dose, which is set on the controller, the 4-20 mA proportional relay output is activated, which regulates the operation of the pump frequency converter.
In this case, the maximum value of the analog signal is 20 mA, and the metering pump operates at maximum capacity. When the value of the chlorine dose is close to the value set on the controller, the signal value decreases proportionally and when the set value is reached, it is equal to 4 mA. In this case, the controller relay is switched off, and the frequency converter of the metering pump stops in standby mode.
Calculation of the consumption of sodium hypochlorite (NaClO)