Yeast for alcohol, whisky, wine and beer
Yeast - single-celled organisms that are common in nature; they are found in the soil, on plants, in various substrates containing sugar.
The widespread use of yeast in industry is based on its ability to cause alcoholic fermentation - the conversion of sugar into ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide.
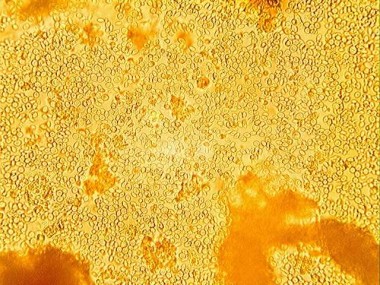
The shape of yeast cells is more often rounded, Oval-ovate or elliptical, less often cylindrical and lemon-shaped. There are yeast of a special shape - sickle-shaped, arrow-shaped, triangular. The size of yeast cells usually does not exceed 10-15 microns.
The shape and size of yeast can vary significantly depending on the conditions of development, as well as on the age of the cells.
The structure of yeast cells is similar to that of fungal cells. Yeast has a true nucleus separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear bilayer membrane, the endoplasmic reticulumum, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, mitochondria, ribosomes, vacuoles.
The composition of the cell wall (shell) in most yeasts includes mainly (up to 60-70% of the dry weight) hemicellulose and in small amounts - proteins, lipids, chitin.
Reproduction of yeast. Budding is the most characteristic and widespread vegetative method of yeast reproduction, only some yeasts reproduce by division.